Home > E. Pathology by systems > Cardiovascular system > Heart > endocardial fibroelastosis
endocardial fibroelastosis
MIM.305300 MIM.226000
Wednesday 17 March 2004
Digital cases
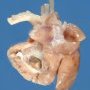
![]() Case 118 : Fibroelastosis of the endocard
Case 118 : Fibroelastosis of the endocard
Definition: Endocardial fibroelastosis (or endomyocardial fibroelastosis) is a condition characterized by widespread thickening of the mural endocardium due to proliferation of collagen and elastic fibers.
The border between the overgrown endocardium and the adjacent myocardium is usually clearly defined. The left ventricle is the chamber of the heart most frequently affected. Nom. 1943, Weinberg and Himelfarb.
Endomyocardial fibroelastosis is a cause of unexplained childhood cardiac insufficiency. It results from diffuse thickening of the endocardium leading to dilated myocardiopathy in the majority of cases and restrictive myocardiopathy in rare cases. It may occur as a primary disorder or may be secondary to another cardiac malformation, notably aortic stenosis or atresia.
The incidence at birth is estimated at 1 in 5 000. In the majority of cases, endomyocardial fibroelastosis is diagnosed at between 3 and 6 months of age. The cardiac insufficiency may be acute with a severe prognosis or chronic.
The primary form is mainly sporadic but 10% of cases are familial with all possible modes of transmission (autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, X-linked).
The underlying cause of the sporadic cases is unknown: it may be associated with an antenatal viral infection, subendocardial ischemia or metabolic anomalies. Treatment is the same as that used for cardiac insufficiency.
Synopsis
![]() endocardial thickness increase
endocardial thickness increase![]() endocardial fibrosis associating collagen fibers and elastic fibers
endocardial fibrosis associating collagen fibers and elastic fibers![]() endocardial calcifications (calcified endocardial fibroelastosis) (3051147, 13915097, 13739516, 9440110)
endocardial calcifications (calcified endocardial fibroelastosis) (3051147, 13915097, 13739516, 9440110)
Etiology
![]() primary
primary
- X-linked endocardial fibroelastosis (MIM.300183) (TAZ mutations at Xq28)
- autosomal recessive endocardial fibroelastosis
- Marles-Chudley syndrome (ulnar agenesis and endocardial fibroelastosis association) (MIM.276822)
- MTTL2 mitochondrial cardiomyopathy (MIM.590055)
![]() secondary
secondary
- cardiac malformations
- left ventricular outflow obstruction
- aortic atresia
- aortic valve stenosis (aortic stenosis)
- mitral valve hypoplasia
- left ventricle hypoplasia
- left ventricular outflow obstruction
- mitral incompetence and coarctation of abdominal aorta (MIM.226100)
- LEOPARD syndrome (MIM.151100)
- Ebstein anomaly (1636604)
- L-transposition of the great arteries with Ebstein anomaly (9688767)
- anomalous right coronary artery arising from the pulmonary trunk (4029950)
- inherited human cardiomyopathies
- MTTL2 mitochondrial cardiomyopathy (MIM.590055)
- MYH7 germline mutations (beta-cardiac myosin heavy chain mutation) (17019812)
- familial cardiomyopathy with conduction disturbance (MIM.108770)
- isolated noncompaction of ventricular myocardium (INVM) or left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) (MIM.300183)
- twin-twin transfusion syndrome (9724339)
- viral infections
- coxsackie virus myocarditis
- metabolic diseases
- Barth syndrome (cardioskeletal myopathy with neutropenia) (MIM.302060) (TAZ mutations at Xq28)
- systemic carnitine deficiency (MIM.212140)
- Hurler syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis type IH) (MIM.607014) (2500843)
- mucopolysaccharidosis type VI (3109796)
- dysimmunity and auto-immunity
- neonatal lupus with auto-antibodies anti-SSA/Ro and anti-SSB/La antigens (16980725, 16218462)
Associations
![]() communicating hydrocephalus and congenital cataracts (HEC syndrome) (MIM.600559) (7747788)
communicating hydrocephalus and congenital cataracts (HEC syndrome) (MIM.600559) (7747788) ![]() ulnar agenesis with oligodactyly (MIM.276822) (2248295)
ulnar agenesis with oligodactyly (MIM.276822) (2248295)![]() faciocardiorenal syndrome (horseshoe kidneys, severe mental retardation, characteristic facies (broad nasal bridge, large chin, open mouth), and heart defect (conduction defects, cardiac enlargement, endocardial fibroelastosis) (MIM.227280)
faciocardiorenal syndrome (horseshoe kidneys, severe mental retardation, characteristic facies (broad nasal bridge, large chin, open mouth), and heart defect (conduction defects, cardiac enlargement, endocardial fibroelastosis) (MIM.227280)
See also
![]() histiocytoid cardiomyopathy
histiocytoid cardiomyopathy![]() endocardial fibrosis
endocardial fibrosis